Hey Folks!
Today this post would be, as I said in my last post, about Wired/ Guided Transmission Media Technologies. As a plain fact to remember, guided media are those where the transmissions they carry can be guided. The Ethernet cable that connects to your PC Modem? That's an example of Guided Transmission Media. The Music Player in your car that plays up songs for you from the local radio? NOT an example of Guided Transmission Media. In this case the radio waves are spread throughout the atmosphere and your car just receives and plays that signal. The others going around with you can play the same signal. There is no amount of direction given to these signals and are just spread out for our equipments to receive.
In general, any type of wired transmission media can be safely assumed to be an example of Guided Transmission Media.
There are several types of Guided Transmission Media. Let us study them one by one.
Today this post would be, as I said in my last post, about Wired/ Guided Transmission Media Technologies. As a plain fact to remember, guided media are those where the transmissions they carry can be guided. The Ethernet cable that connects to your PC Modem? That's an example of Guided Transmission Media. The Music Player in your car that plays up songs for you from the local radio? NOT an example of Guided Transmission Media. In this case the radio waves are spread throughout the atmosphere and your car just receives and plays that signal. The others going around with you can play the same signal. There is no amount of direction given to these signals and are just spread out for our equipments to receive.
In general, any type of wired transmission media can be safely assumed to be an example of Guided Transmission Media.
There are several types of Guided Transmission Media. Let us study them one by one.
Twisted Pair Cable
The most common form of wiring in data communication application is the twisted pair cable. As a Voice Grade Medium (VGM), it is the basis for most internal office telephone wiring. It consists of two identical wires wrapped together in a double helix. Problems can occur due to the differences in the electrical characteristics between the pair (e.g. length, resistance and capacitance). For this reason, LAN applications will tend to use a higher quality cable known as Data Grade Medium (DGM). Different types and categories of twisted-pair cable exist, but they all have two things in common:
- The wires come in pairs
- The pairs of wires are twisted around each other
 |
| Advantages and Disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cable |
 |
| Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable |
Types of Twisted Pair Cable
There are two types of twisted pair cables available. These are:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable: UTP cabling is used for a variety of electronic communications. It is available in the following five categories:
- CAT1: Voice-Grade communications only; No data transmission
- CAT2: Data-grade transmission up to 4 Mbps
- CAT3: Data-Grade transmission up to 10 Mbps
- CAT4: Data-grade transmission up to 16 Mbps
- CAT5: Data-grade transmission up to 1000 Mbps
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
The UTP cables can have a maximum segment length of 100 meters.
Despite the shortcomings, Optical Fiber is an important technology and will be a very attractive transmission medium even in the future indeed.
So thats'd be all for today, thanks for reading. Do check out other posts on our blog. Thanks a lot! :)
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
This type of cables comes with shielding of individual pairs of wires, which further protects it from external interference. But these also, like UTP, can have a maximum segment length of 100 meters. The advantage of STP over UTP is that it offers greater protection from interference and crosstalk due to shielding. But it is definitely heavier and costlier than UTP and requires proper grounding at both ends.
 |
| Shielded Twisted Pair Cable; Image Courtesy: technologyuk.net |
Coaxial Cable
This type of cable consists of a solid wire core surrounded by one or more foil or wire shields, each separated by some kind of plastic insulator. The inner core carries the signal, and the shield provides the ground. The coaxial cable has high electrical properties and is suitable for high speed communication. While it is less popular than twisted pair, it is widely used for television signals. In the form of (CATV) cable, it provides a cheap means of transporting multi-channel television signals around metropolitan areas. It is also used by large corporations in building security systems. The data transmission characteristics of coaxial cable are considerably better than those of twisted pair. This opens the possibility of using it as the basis for a shared cable network, with part of the bandwidth being used for data traffic.
 |
| Advantages and Disadvantages of Coaxial Cables |
Types of Coaxial Cables
The two most commonly used types of coaxial cables are Thicknet and Thinnet.
- Thicknet: This form of coaxial cable is thicker than Thinnet. The Thicknet coaxial cable segments (while joining nodes of a network) can be up to 500 meters long.
- Thinnet: This form of coaxial cable is thinner and it can have maximum segment length of 185 meters i.e. using these cables, nodes having maximum distance of 185 meters can be joined.
Diagrammatically,
we can see the basic construction of a coaxial cable, a Thicknet Coaxial cable
and a Thinnet Coaxial cable here below:
 |
| Different layers in a Coaxial Cable; Image Courtesy: technologyuk.net |
Also lets see the Thicknets and Thinnets side by side.
 |
| Thicknet; Image courtesy: technologyuk.net |
 |
| Thinnet; Image Courtesy: technologyuk.net |
Optical Fibre
Optical Fibers consist of thin strands of glass or glass like material which are so constructed that they carry light from a source at one end of the fiber to a detector at the other end. The light sources used are either light emitting diodes (LEDs) or LASER Diodes (LDs). The data to be transmitted is modulated onto the light beam using frequency modulation techniques. The signals can then be picked up at the receiving end and demodulated. The bandwidth of the medium is potentially very high. For LEDs, this range is between 20-150 Mbps and higher rates are possible using LDs.
The fiber cable consists of four pieces:
- The Core, i.e. the glass or plastic through which the light travels.
- The Cladding, which is a covering of the core that reflects light back to the core.
- Primary Buffer or the protective coating which protects the fiber cable from hostile environment.
- Jacket or the outer covering of the cable.
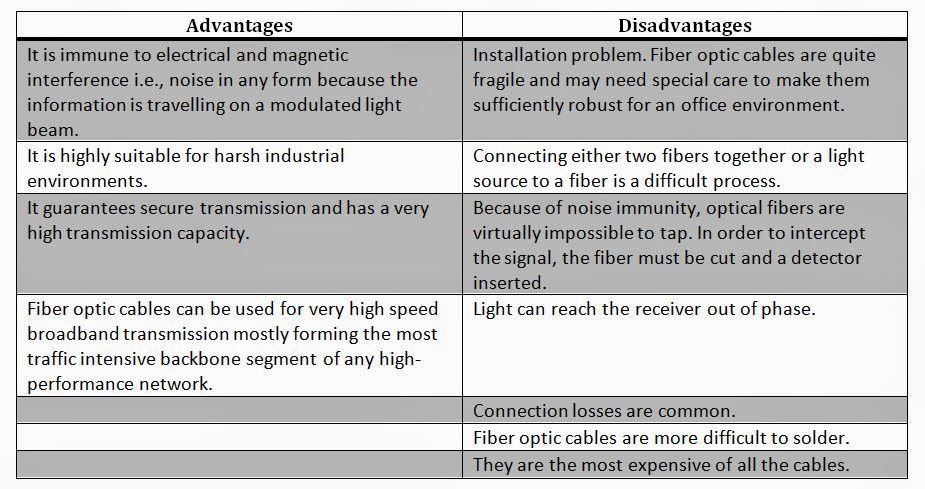 |
| Advantages and Disadvantages of Optical Fibre Cables |
Types of Optical Fibre Cables
Fiber Optic cables can be either Single Mode that supports a segment length of up to 2 kilometers and bandwidth of up to 100 Mbps or Multi Mode with a segment length of 100 kilometers and bandwidth 2 Gbps.
 |
| A Bunch of Optical Fibres |
So that was it. Lets now revise all we learnt.
 |
| Guided Media Compared |
So thats'd be all for today, thanks for reading. Do check out other posts on our blog. Thanks a lot! :)


0 comments:
Post a Comment